XAU/USD Buy & Sell Signals with Pivot Points
Forex Position Size Calculator
Forex Basics – Learn How Forex Trading Works
What is a Currency Pair ?
A currency pair represents the value of one currency quoted against another.
Example
EUR/USD = 1.10 -> Means 1 Euro equals 1.10 US Dollars
Base and Quote Currency
Base Currency : The first currency listed in the pair.
Quote Currency : The second currency listed in the pair.
ISO Currency Codes
Each currency in Forex has a unique three-letter ISO code, created by the İnternational Organization for Standardization (ISO) .
Example :
| Country | Currency | ISO Code |
| United States | Dollar | USD |
| Eurozone | Euro | EUR |
| Japan | Yen | JPY |
| Canada | Canadian Dollar | CAD |
| United Kingdom | Pound Sterling | GBP |
Example : Understanding USD/CAD
Currency Pair : USD/CAD = 1.35
Base Currency : USD (US Dollar)
Quote Currency : CAD (Canadian Dollar)
USD/CAD = 1.35 means 1 USD = 1.35 CAD

Forex Major & Cross Currency
| Category | Explanation | Examples |
| Major Currencies | The most traded and liquid currencies in the world | USD (US Dollar), EUR (Euro), JPY (Japanese Yen), GBP (British Pound), AUD (Australian Dollar), CAD (Canadian Dollar), CHF (Swiss Franc) |
| Major Currency Pairs | Currency pairs that always include the USD as base or quote. | EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CHF, USD/CAD, AUD/USD, NZD/USD |
| Cross Pair | Currency pairs that do not include the USD. | EUR/GBP, CAD/JPY, AUD/NZD |
| Nickname Examples | Common trader nicknames for popular pairs. | GBP/USD = The Cable, USD/CAD = Loonie, AUD/USD = Aussie, USD/CHF = Swissy |
Market Structure & İnterbank Market
| Category | Explanation | Examples |
| Market Structure | The Forex market operates OTC (Over The Counter), meaning trades are conducted directly between parties without a central exchange. | No central exchange like NYSE or NASDAQ. |
| Price Variation | Because of the decentralized OTC structure, execution prices vary between brokers and platforms. | Broker A: 1.3520, Broker B: 1.3523 |
| İnterbank Market | The core level of the forex market where large banks trade currencies directly. | Example: Citibank trades EUR/USD with Deutsche Bank. |
| Trading Platforms | Banks use EBS (Electronic Broking Services) or Thomson Reuters Dealing System for direct interbank transactions. | EBS – used for USD/JPY, EUR/USD etc. |
| Access Level | Only large financial institutions have access to the interbank market — not retail traders. | JP Morgan, HSBC, Barclays |
| Market Participants | Main participants include FX Dealers, Hedge Funds, Forex Brokers, and Retail ECNs. | Retail ECNs (Electronic Communication Networks) connect traders to liquidity providers. |
Price Terminology
| Term | Explanation |
| Spot Price | A currency pair’s current market price. |
| Order Book | List of all open buy and sell orders. |
| Bid Price | List of all open buy and sell orders. |
| Ask Price | Price at which you can buy right now. |
| Spread |
Difference between bid and ask price. |
Pips and Lots
| Term | Explanation |
| Point | Minimum price movement. |
| Pip | Standard smallest price change. |
| Pipette | Fractional pip (1/10 of a pip). |
| Standard Lot (100, 000 units) | 100,000 units of base currency. |
| Mini Lot (10,000 units) | 10,000 units of base currency. |
| Micro Lot (1,000 units) | 1,000 units of base currency. |
Pip Value Calculation
| Concept | Explanation |
| Example Pair | USD/CAD = 1.35251 |
| Contract Pair (1 Lot) | 100,000 USD × 1.35251 = 135,251 CAD |
| İf Price Moves Up 1 Pip | New Price = 1.35261 + If it increases by 1 pip |
| New Contract Value | 100,000 USD × 1.35261 = 135,261 CAD |
| Pip Value in Quote Currency | 135,261 − 135,251 = 10 CAD |
| Pip Value in Base Currency | 10 ÷ 1.35251 = 7.39 USD |
| Note 1 | Pip value is always in the quote currency |
| Note 2 | Pip value depends on lot size |
Leverage
| Concept | Explanation |
| Defination | Funds loaned to your by your broker. |
| Purpose | Allows you to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital |
| Maximum Leverage | Brokers can loan up to 1000x your capital |
| Effect | İncreases both potential prfit and potential loss. |
Leverage Levels
| Leverage | Margin Required (%) | Margin for Lot ($) |
| 1:1 | 100% | $100,000 |
| 2:1 | 50% | $50,000 |
| 10:1 | 10% | $10,000 |
| 50:1 | 2% | $2,000 |
| 100:1 | 1% | $1,000 |
| 200:1 | 0.5 % | $500 |
| 400:1 | 0.25 % | $250 |
| 800:1 | 0.125% | $125 |
| 1000:1 | 0.1 % | $100 |
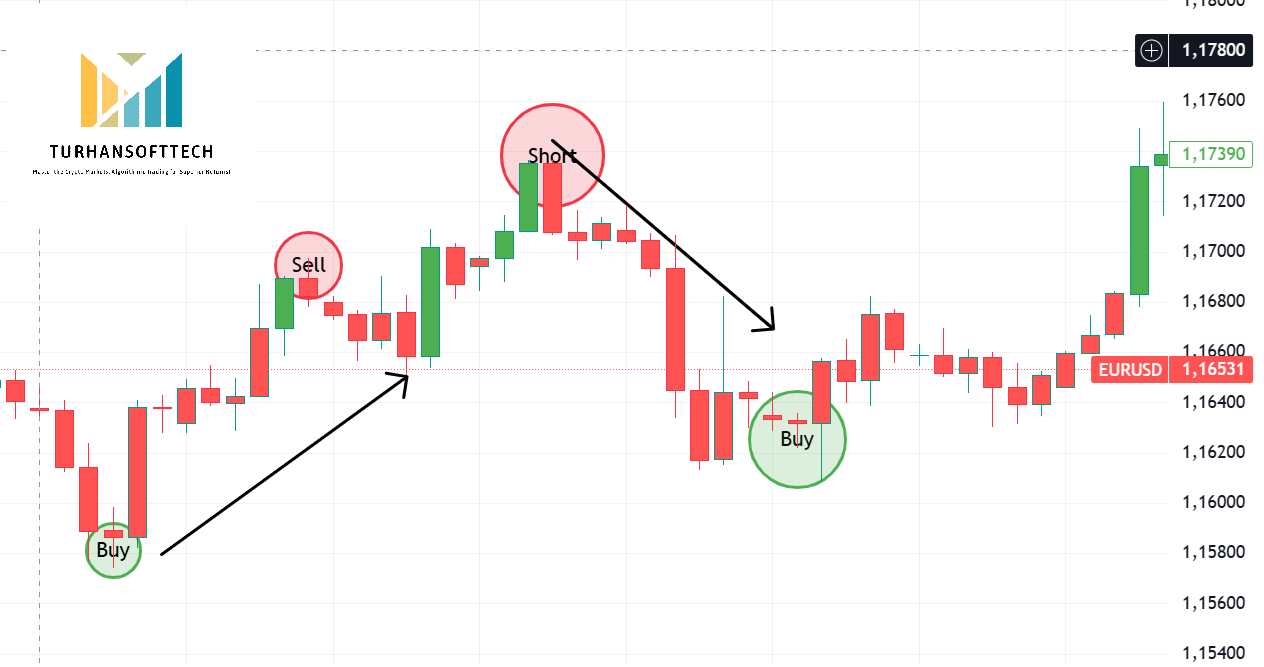
Short Selling
| Concept | Explanation |
| Defination | The sale of an asset that the seller does not own, done by borrowing the asset. (Wikipedia) |
| Purpose | To profit from a decline in the asset’t price |
| Mechanism |
1️⃣ Borrow the asset 2️⃣ Sell it at a higher price 3️⃣ Buy it back later at a lower price 4️⃣ Return the borrowed asset. |
| Profit Example | You short EUR/USD at 1.1000 → It drops to 1.0900 → You gain 100 pips |
| Risk | Unlimited — if the price rises instead of falling, losses can grow indefinitely. |
| Used in | Forex , Stocks , Commodities , Derivatives |
Broker and Orders
| Term | Explanation |
| Broker | Entity that facilitates the execution of your order. |
| Order | İnstructionss to buy/sell a quantity of a product |
| Regulated Broker | Broker under legal supervision by authorities. |
| Transparency | Clear visibility of fees, spreads, and execution. |
| Alignment of Interests | Broker profits when you profit |
| Low Fees | Lower trading comission and spreads. |
| Leverage | Funs loaned by broke to increase positions size |
| Good Platform | Reliable and user-friendly trading interface. |
| Support | Technical and customer assisstance. |
A Book vs B Book
| Model | Description |
| A Book (ECN Model) | Broker sends your orders directly to major liquidity providers. |
| B Book (Market Maker Model) | Broker takes the opposite side of your trade (can hedge or not). |
ECN Brokers and Comissions
- ECN brokers charge commission per trade instead of widening spreads.
- They offer direct market access and higher transparency.
Trading Platform
| Metatrader 4 (MT4) | The most widely used trading platform in the world. |
| Most Used Platfrom | Preferred by traders globally due to its reliability. |
| Programming Language | Uses MQL4, a popular scripting language for algorithmic trading. |
| Kind of Old (15 years) | Developed around 2005–2006, still functional but aging |
Ways of Analysis
| Technical Analysis | The study of price and volume charts to identify trading opportunities. |
| Fundemental Analysis | The study of economic, political, and financial factors affecting a currency or asset. |
| Purpose of Technical Analysis | To identify entry and exit points and improve profitability by analyzing market patterns. |
| Application in Strategy | Used to systematize trades — making trading decisions consistent and data-driven. |
Risk Management
What’s Risk ?
An action or an activity that has a potential to go wrong.
Risk Management Techniques
| Risk Acceptance : Acknowledging the risk and choosing to proceed. |
| Risk Avoidance : Taking steps to completely avoid the risk. |
|
Risk Reduction : Minimizing potential impact or likelihood.
|
| Risk Transfer : Shifting risk to another party (e.g., insurance). |
Money Management
The larger the percentage of your account lost, the higher the percentage gain required to break even. For example, if you lose 50% of your account, you need a 100% gain to return to the original balance.
If you want, I can also make a clear visual chart showing loss vs. required gain.
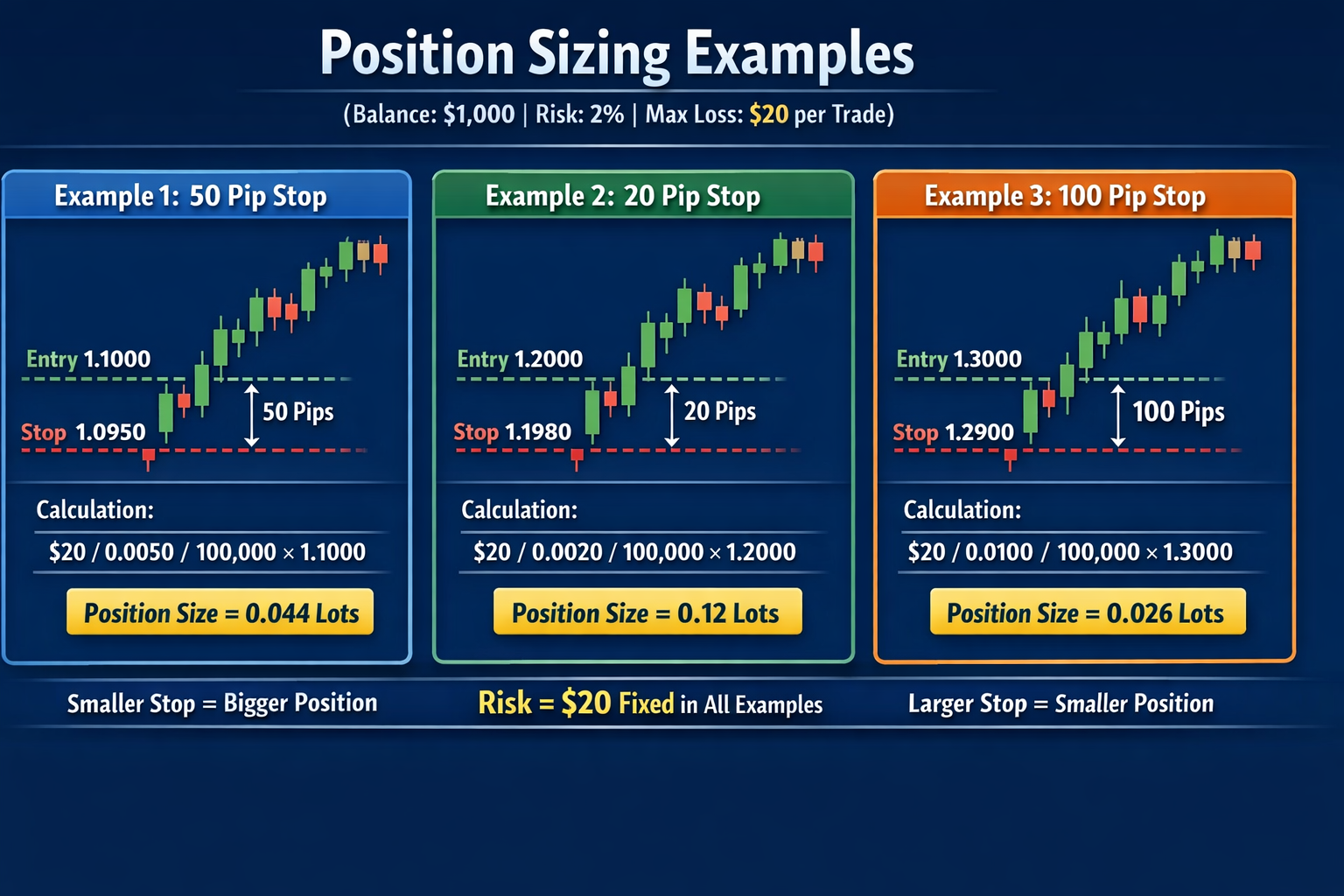
Position Sizing
| Position Sizing | Determines how much to risk per trade |
| Maximum Loss per Trade | ~2% of account |
| Steps | Step by step guide to calculate position size |
|
|
| Formula | Position Size = ((Max Loss $) / (Entry Price – Stop Loss Price)) / 100,000 × Entry Price |
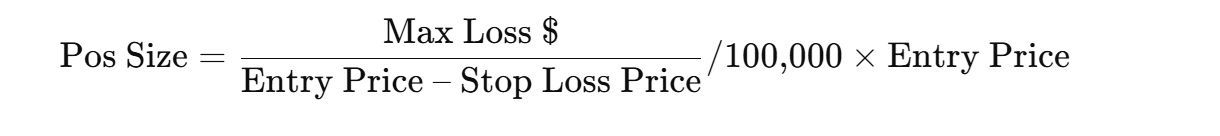
Batting Average & Win/Loss Ratio
| Batting Average |
The percentage of trades that are profitable Indicates how often your trades are successful. Higher batting average means more winning trades |
60 profitable trades out of 100 → 60% |
| Win/Loss Ratio |
Ratio of average profit per winning trade to average loss per losing trade. Shows the size of your wins relative to losses. A ratio >1 means your profitable trades earn more than your losses |
Avg profit per win: $200, Avg loss per loss: $100 → Win/Loss Ratio = 2 |
